where is the z test package for r|z test in r : manufacturers z.test(x,sigma.x=1) # Two-sided one-sample z-test where the assumed value for # sigma.x is one. The null hypothesis is that the population # mean for 'x' is zero. The alternative hypothesis states # that it is either greater or less than zero. web'loiras' Search - XNXX.DEV. Results for : loiras. Report. Mode. Default. Period. Ever. Length. All. Video quality. All. Viewed videos. Show all.
{plog:ftitle_list}
webThe answer to your question may not always be the one you wanted, but that doesn’t mean it is wrong. A conclusive answer isn’t always possible. When in doubt, ask people to cite .
z.test(x,sigma.x=1) # Two-sided one-sample z-test where the assumed value for # sigma.x is one. The null hypothesis is that the population # mean for 'x' is zero. The alternative hypothesis states # that it is either greater or less than zero. The syntax of z- test in R is: z.test(x, y, alternative='two.sided', mu=0, sigma.x=NULL, sigma.y=NULL,conf.level=.95) Now we can conduct one sample test and two sample tests in R. Here we provide the vector(s) and also .
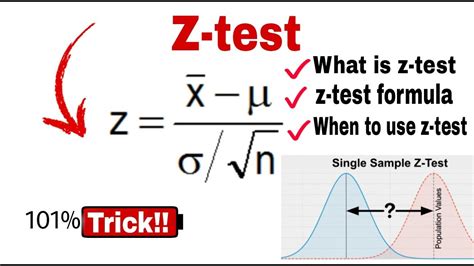
A one-sample z-test is used to determine whether the population mean is equal or different from a predefined standard (or theoretical) value of mean when population standard deviation is . The Z test is a fundamental hypothesis test that allows us to conclude population parameters based on sample data. This tutorial will provide step-by-step guidance on conducting one and two sample Z tests in R, .z.test: Z test for known population standard deviation. Description. Compute the test of hypothesis and compute confidence interval on the mean of a population when the standard .Z-test Description. This function is based on the standard normal distribution and creates confidence intervals and tests hypotheses for both one and two sample problems. Usage .
You can use the z.test () function from the BSDA package to perform one sample and two sample z-tests in R. This function uses the following basic syntax: z.test(x, y, . The one-sample Z-test is a statistical test used to determine if there is a significant difference between the mean of a single sample and a known population mean.One sample Z-tests. In this vignette, we work through an example Z-test, and point out a number of points where you might get stuck along the way.
Currently, I am using the r 4.0.5 version, and while doing z test analysis the needed package BSDA is not present. Although I tried to install it from different sources but could not succeed. Anyone can come up with the idea, so I can proceed with the . This tutorial explains how to perform a one sample and two sample z-test in R, including several examples. Top Posts. How to Create a Stem-and-Leaf Plot in SPSS. . You can use the z.test() function from the BSDA package to perform one sample and two sample z-tests in R. This function uses the following basic syntax: z.test .This initial setup is usually something you do once per package. However, even in a package that already uses testthat, it is safe to run use_testthat(3), when you’re ready to opt-in to testthat 3e.. Do not edit tests/testthat.R!It is run during R CMD check (and, therefore, devtools::check()), but is not used in most other test-running scenarios (such as devtools::test() or devtools::test .
z test in r
Null Hypothesis. For the one-sample z-test, the null hypothesis is that the mean of the population from which x is drawn is mu.For the standard two-sample z-test, the null hypothesis is that the population mean for x less that for y is mu.For the paired z-test, the null hypothesis is that the mean difference between x and y is mu.. The alternative hypothesis in each case indicates the .Then, power and sample size analysis is computed for the Z test. Continue reading → . delta = (ha-h0)) # Using the pwr package pwr.norm.test(d = (ha - h0)/sigma, n = 20, sig.level = 0.05, alternative = "greater") ### Sample size analysis # Using the self-made function sampleSizeZtest(sigma = sigma, power = 0.8, delta = (ha-h0)) # Using the .
Procedure to perform Two Proportion Z-Test in R. Step 1: Define the Null Hypothesis and Alternate Hypothesis. Step 2: Decide the level of significance α (alpha). . What package is needed for the t-test in R? The R Stats Package is needed to do a t-test in R. Summary.
Null Hypothesis. For the one-sample z-test, the null hypothesis is that the mean of the population from which x is drawn is mu.For the standard two-sample z-test, the null hypothesis is that the population mean for x less that for y is mu.For the paired z-test, the null hypothesis is that the mean difference between x and y is mu.. The alternative hypothesis in each case indicates the .
Details. Cohen's d reported when argument effsize = TRUE is based on the population standard deviation specified in sigma or the square root of the population variance specified in sigma2.In a one-sample and paired-sample design, Cohen's d is the mean of the difference scores divided by the population standard deviation of the difference scores (i.e., equivalent to Cohen's d_z .
What is the minimum sample for z-test? A z-test can only be used if the population standard deviation is known and the sample size is 30 data points or larger. Otherwise, a t-test should be employed. What is the application of z-test? It is also used to determine if there is a significant difference between the mean of two independent samples. What is Z-score. In short, the z-score is a measure that shows how much away (below or above) of the mean is a specific value (individual) in a given dataset. In the example below, I am going to measure the z value of body mass index (BMI) in a dataset from NHANES. Get the data and packages. Loading packages and creating the dataset:This function is based on the standard normal distribution and creates confidence intervals and tests hypotheses for both one and two sample problems.
Many introductory statistical texts introduce inference by using the Z test and Z based confidence intervals based on knowing the population standard deviation. Most statistical packages do not include functions to do Z tests since the T test is usually more appropriate for real world situations. This function is meant to be used during that .The test gives a p-value of 1, indicating there is no evidence to reject the null hypothesis that the true proportion is \(p\). Two proportions Z test (difference of proportions) The two-sample proportion test compares proportions between two independent groups. It assesses whether the proportions in these groups significantly differ from each .This is a entry level course to learn stats and R. The one-sample Z-test in R. We can run such a test in R, using the package BSDA, and its function z.test. Lets try it.
The following example shows how to perform a Wald test in R. Example: Wald Test in R. For this example, we’ll use the built-in mtcars dataset in R to fit the following multiple linear regression model: mpg = β 0 + β 1 disp + β 2 carb + β 3 hp + β 4 cyl. The following code shows how to fit this regression model and view the model summary:We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Null Hypothesis. For the one-sample z-test, the null hypothesis is that the mean of the population from which x is drawn is mu.For the standard two-sample z-test, the null hypothesis is that the population mean for x less that for y is mu.For the paired z-test, the null hypothesis is that the mean difference between x and y is mu.. The alternative hypothesis in .
This function is based on the standard normal distribution and creates confidence intervals and tests hypotheses for both one and two sample problems. Power analysis for a one sample z-test Description. A power analysis for a one sample z-test.The function requires \alpha, \sigma, the effect size, the type of test (one tailed or two-tailed), and either power (1 - \beta) or n (sample size). If n is provided, then power is calculated. Conversely, if one provides power, but not n, then the required n is calculated.Function in R for z-test. z.test() function in R from the BSDA library is used to perform a one-sample z-test for mean. Install BSDA for z-test for mean. If you don’t have the BSDA library installed then use the below command on the R Editor for BSDA library installation. install.packages("BSDA") The z.test() function uses the following basic .
However statistical packages often do not include functions to do z-tests since the t-test is usually more appropriate for real world situations. This function is meant to be used during that short period of learning when the student is learning about inference using z-procedures, but has not learned the t-based procedures yet. Many introductory statistical texts introduce inference by using the Z test and Z based confidence intervals based on knowing the population standard deviation. Most statistical packages do not include functions to do Z tests since the T test is usually more appropriate for real world situations. This function is meant to be used during that .
An R function called z.test() would be great for doing the kind of testing in which you use z-scores in the hypothesis test. . Although you can find one in other packages, it's easy enough to create one and learn a bit about R programming in the process. The function will work like this: > IQ.data <- c(100,101,104,109,125,116,105,108,110)R Fundamentals Level-up your R programming skills! Learn how to work with common data structures, optimize code, and write your own functions. Big Data with R Work with big data in R via parallel programming, interfacing with Spark, writing scalable & efficient R code, and learn ways to visualize big data. Machine Learning with R
This is a entry level course to learn stats and R. The two-sample Z-test in R. We can run such a test in R, using the package BSDA, and its function z.test. Lets try it.
z test for mean r
Tests the significance of a single correlation, the difference between two independent correlations, the difference between two dependent correlations sharing one variable (Williams's Test), or the difference between two dependent correlations with different variables (Steiger Tests).
Implement basic z-test for illustrative purposes Description. Imlements a z-test similar to the t.test function Usage simple.z.test(x, sigma, conf.level=0.95)
o quantitative
one quantitative observation
one quantitative
what is z in r
webUltra Academia - Jardim Botânico (23) . Q 3 · Sh Jardim Botânico/Condomínio Solar de Brasília, 23/26 Aulas: Abdominais · Alongamento · Ergometria · Fit Dance · Funcional · Musculação Espaço com localização privilegiada, fácil acesso, oferecendo o desenvolvimento de atividades físicas que proporcionem prazer, satisfação e bem .
where is the z test package for r|z test in r